Curiosities and Challenges about Natural Sciences
Do you like Natural Sciences?
Would you like to see more curiosities like these..
Natural Sciences is short for Biology, Physics, Chemistry and Geography, and its main areas of study are natural....
Reproduction is the function that allows the continuity of life and is common to all living beings. In humans,..
Adolescence begins with puberty - from 8 to 14 years old, in girls, and from 9 to 15 years old, in boys. This is the....
So.. How about a Challenge on the Best Quiz Platform in the World?
Exploring science is discovering the secrets of the universe
Get to know a little about everything and bet on your knowledge in incredible challenges and duels..
Join the betspot.zone community, accumulate bts (bets) and even compete for prizes..
Discover some interesting facts about Natural Sciences..
science Quiz - science Curiosities - science Challenge - academic Quiz - academic Curiosities - academic Challenge - maisciencias Quiz - maisciencias Curiosities - maisciencias Challenge - school Quiz - school Curiosities - school Challenge - maisciências Quiz - maisciências Curiosities - maisciências Challenge - - Frequently asked questions about Natural Sciences
World Turtle

World Turtle Day is celebrated on May 23rd every year. This date was created with the aim of raising awareness about the conservation of sea turtles and their habitats. Sea turtles face several threats, such as bycatch, habitat destruction, marine pollution and illegal hunting, which have brought many species to a state of danger of extinction. World Turtle Day serves as an opportunity to highlight the importance of protecting these incredible creatures and promoting conservation action around the world.
celebrate in May 23
publicity
World Brain
World Brain Day is celebrated on July 22nd . This date was created by the World Federation of Neurology (WFN) to raise awareness of the importance of the brain in human health and well-being. The goal is to promote education about the brain, encourage research and innovation in the field of neuroscience, and highlight the importance of preventing and treating brain disorders. During World Brain Day, events are organized around the world, such as lectures, workshops, awareness campaigns and educational activities for people of all ages. The main focus is to promote brain health and provide information on how to keep the brain healthy throughout life.
celebrate in July 22
World Nature Conservation

World Nature Conservation Day is celebrated on July 28th . This date was established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1972, during the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, also known as the Stockholm Conference. The objective of World Nature Conservation Day is to raise awareness about the importance of preserving and protecting biodiversity and our planet's natural ecosystems. It is an opportunity to highlight the environmental challenges faced globally and promote individual and collective actions for nature conservation. On this day, several activities are carried out, such as environmental education campaigns, tree planting, cleaning of natural areas, lectures and events to promote sustainable practices.
celebrate in July 28
International Octopus

International Octopus Day is celebrated on October 8 , a date created by Octopus News Magazine Online (TONMO) in honor of these incredible animals, which have eight appendages. The choice of the day coincides with mating season, making it an ideal time to raise awareness about octopuses, known for their intelligence and camouflage abilities. With 90% of their bodies composed of muscles, they have three hearts and around five hundred million neurons. The celebration aims to highlight the importance of octopuses in marine ecosystems and promote the protection of their habitats. Events are organized around the world to educate the public about the threats these animals face, such as pollution and overfishing.
celebrate in October 8
publicity
The Kingdom Plantae (Kingdom of Plants)
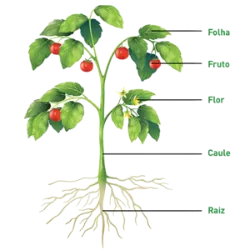
The Kingdom Plantae (Kingdom of Plants) encompasses eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic (photosynthetic) beings with a cell wall rich in cellulose. Main features: Photosynthesis: They produce their food using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide. Reproduction: Can be sexual (with gametes) or asexual (cloning, spores, budding). Classification: Bryophytes: Small, without conducting vessels (e.g. mosses). Pteridophytes: They have vessels, but no seeds (e.g.: ferns). Gymnosperms: "Naked" seeds, without fruit (e.g. pine trees). Angiosperms: Seeds protected by fruits, flowers (e.g. fruit trees). Plants are essential for environmental balance, providing oxygen, food and shelter. In education, studying this kingdom develops notions about ecology, biodiversity and sustainability.
The oxygen
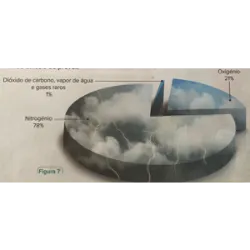
The oxygen generated by these living beings slowly accumulated in the atmosphere, which changed its composition and created, around 400 million years ago, the conditions necessary for the formation of an ozone layer. This layer is capable of filtering ultraviolet radiation, thus allowing living beings to colonize terrestrial environments outside of water. The enrichment of the atmosphere with oxygen, produced in photosynthesis, allowed this gas to become available and be used by living beings in cellular respiration, which in turn releases the carbon dioxide consumed in photosynthesis into the atmosphere. The Earth's atmosphere has undergone continuous changes in its composition over geological time, responsible for drastic climate changes and mass extinctions. Currently, it is human activities that produce a growing and global impact on the atmosphere with consequences that are still difficult to predict.
The Earth
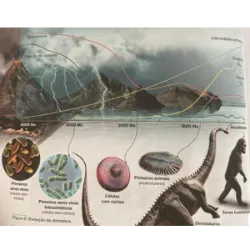
The Earth was an uninhabitable place with no breathable air for hundreds of millions of years after its formation. Over time, however, it developed an atmosphere that was quite different from the one we know today. The primitive atmosphere was composed of methane, ammonia, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapour, but there was no oxygen. Oxygen only appeared in the atmosphere due to its release by living beings, namely through photosynthesis. The first photosynthetic beings were not plants or algae, as they did not yet exist. The first living beings to carry out photosynthesis and release oxygen into the atmosphere were microorganisms similar to today's bacteria that began to appear in the primitive oceans, more than 3,000 million years ago.
publicity
The Importance of the Atmosphere for Life

Atmosphere: The atmosphere plays crucial roles in sustaining life, such as filtering harmful ultraviolet rays through the ozone layer , protecting against meteorite impacts , and regulating the environmental temperature compatible with life through the greenhouse effect . These characteristics help create suitable conditions for life. The existence of the atmosphere is possible due to the size and mass of the Earth, which generate sufficient gravitational attraction to keep this layer of gases attached to its surface. Without this gravitational force, the atmosphere would disperse into space.
Geosphere dynamics:

Geosphere dynamics: The movement of tectonic plates and the rock cycle are processes that shape landscapes, form soils and create new environments, driving the evolution and diversity of species. Water: The abundance of liquid water is essential for life, as it makes up between 70% and 90% of the body weight of living beings and participates in all their vital processes. Natural environments: The variety of habitats on Earth favors the capacity for adaptation and the growth of biodiversity, increasing the chances of survival and continuity of species.
The Influence of the Moon and the Giant Planets

The Moon and the giant planets: The movement of the Moon around the Earth helps to stabilize the axis of rotation, maintaining a constant tilt, which is crucial for the cycle of the seasons . In addition, the gravitational force of the Moon is responsible for the occurrence of tides and ocean currents , which influence the Earth's climate . The gravity of the giant planets, especially Jupiter, attracts asteroids and comets that could collide with the Earth and cause extinctions . Earth's magnetic field: This field acts as a protective shield, deflecting much of the harmful radiation emitted by the Sun.
publicity
Earth

Earth is the only planet in the Solar System that has the ideal conditions for life as we know it. Some of the factors that make this possible include: the perfect distance from the Sun, the influence of the Moon and the giant planets, the presence of a magnetic field, the dynamism of the geosphere, the abundance of water, the diversity of natural environments and a protective atmosphere. Distance from the Sun: Earth orbits within the habitable zone of the Solar System, at a distance that allows the presence of liquid water on its surface.
Some important events in Earth's history that created the co

Some important events in Earth's history that created the conditions for the emergence of life over thousands of years include: the formation of the planet with impacts from other bodies in the Solar System; the creation of a solid crust, with continents and oceans; the development of an atmosphere with a greenhouse effect; the movement of tectonic plates and volcanic activity; atmospheric electrical phenomena; the formation of simple organic molecules and macromolecules; the emergence of the first primitive cells; the beginning of photosynthesis and the production of oxygen; the creation of the ozone layer and superglaciations that gave rise to new environments.
Earth is a unique and extraordinary planet
Earth is a unique and extraordinary planet, being the common home of all species, where we still enjoy the best conditions of comfort, sustenance and protection for life. However, it was not always like this. The planet we know today is the result of a complex process of transformations that began about 4.6 billion years ago. With the advancement of science and technology, human intelligence has made our species the most dominant, capable of influencing natural processes, consuming large amounts of resources and, thus, shaping the future of the planet. Now, we have the responsibility to ensure the survival of all the species that share the Earth with us.
publicity
The discovery of penicillin: a revolution in medicine
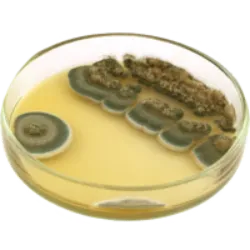
The discovery of penicillin: a revolution in medicine. In 1929, by a stroke of luck, Alexander Fleming found the first antibiotic, penicillin. During World War II, its potential was extensively tested, saving countless lives. Noel Rosa and many other artists could have been saved from tuberculosis if this discovery had occurred earlier. The curious thing is that Fleming, a researcher dedicated to bacteria, left a culture plate forgotten during the summer. By chance, some bread crumbs fell on it, creating fungus. When his colleague Merlin Pryce noticed something strange in the plates about to be discarded, Fleming realized that the fungi had eliminated the bacteria, giving rise to penicillin, a milestone in the history of medicine.
Rocks are natural formations composed of cohesive minerals

Rocks are natural formations composed of cohesive minerals, resulting from geological processes. Minerals, in turn, are solid inorganic substances, with a crystalline structure and defined chemical composition. Unlike organic components, minerals have an ordered arrangement and can form crystals visible to the naked eye, as in granite.
Natural Sciences is short for Biology, Physics

Natural Sciences is short for Biology, Physics, Chemistry and Geography, and its main areas of study are natural history, fundamental laws of nature, structural analysis of the Earth and the forces that control the interaction between organisms. In this course, students examine and study the elements of nature around them, addressing the environment, the life cycle and interactions between living beings. Other subjects addressed include climate change, biodiversity, ecosystems and human influences on nature.
publicity
Reproduction
Reproduction is the function that allows the continuity of life and is common to all living beings. In humans, reproduction is sexual, as it is possible by the union of two sex cells: one female, the oocyte, and the other male, the sperm. When the human being is born, we can only identify the sex of the baby by observing its genitals. Thus, we call these organs primary sexual characters – the penis and the vagina. As we grow, our body undergoes changes in its external appearance – secondary sexual characteristics – which in adolescence already allow us to distinguish between girls and boys.
Adolescence begins with puberty - from 8 to 14 years old

Adolescence begins with puberty - from 8 to 14 years old, in girls, and from 9 to 15 years old, in boys. This is the phase in which not only major physical changes occur, but also psychological and even relational changes. In this phase, the "chemical messengers" - the hormones testosterone, in boys, and estrogen and progesterone, in girls -, which were inhibited in childhood, trigger the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, giving human beings the physical traits they will have in adult life. Sometimes during adolescence, pimples appear on the face. This inflammation and obstruction of the pores of the skin, called acne, is caused by an increased production of sebum (fat) from the sebaceous glands of the skin, due to intense hormonal activity.
The male reproductive system consists of: the testes
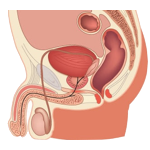
The male reproductive system consists of: the testes, the vas deferens, the seminal vesicles, the prostate and the penis. Starting at puberty, the testes continually produce millions of sperm, the male sex cells. The sperm, together with a fluid from the seminal vesicles and the prostate, form the sperm. The emission of this liquid to the outside of the body is called ejaculation. Seminal vesicles (Produce a viscous fluid); Prostate (Produces the milky and thick liquid that mixes with the seminal fluid, providing the nutritive and transport medium for the sperm); Deferent ducts (carry sperm from the testicles to the penis) Urethra (Channel common to the reproductive and urinary systems); Scrotum (skin pouch that surrounds the testicles); Penis (Organ that conducts sperm to the outside) and Testicles (Located outside the body, inside a bag, the scrotum. They produce sperm).
publicity
The female reproductive system is made up of: the ovaries
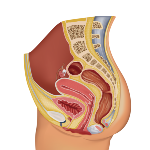
The female reproductive system is made up of: the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, the vagina and the vulva. The ovaries produce the female sex cells called oocytes. The girl has the full amount of oocytes at birth and, as soon as she menstruates, she monthly releases one oocyte from each ovary, alternately. Uterus (muscular organ, hollow, in the shape of an inverted pear and with very elastic walls where the new being will develop. The lower part is called the cervix); Fallopian tubes (Two channels through which the ovaries communicate with the uterus); Ovaries (They are about the size of an almond. Their function is to produce oocytes) and the Vagina (It forms the connection between the uterus and the outside and its walls are elastic and muscular).
In a flowering plant reproduction is sexual and
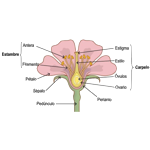
In a flowering plant reproduction is sexual and is carried out by seeds. The flower is the organ responsible for the reproduction of the plant. Its various constituents have different and specific functions that, together, allow the reproduction of the plant, that is, allow the joining of female and male sex cells to give rise to the egg or zygote, the first cell of the new being. Support organs (The receptacle and the peduncle support the entire flower); Protective organs (The corolla - set of petals and the calyx - set of sepals, protect the reproductive organs); Reproductive organs (The carpels - set of female organs and the stamens - set of male organs, are responsible for plant reproduction); the Anthers (they are made up of small sacs full of pollen grains that give rise to male sex cells. The oosphere, the female sex cell, is located in the ovaries).
The transfer of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma
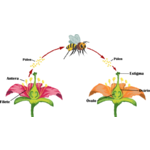
The transfer of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma of the same or another flower is called Pollination, which allows the meeting between the male sex cell and the female sex cell. Pollination agents are responsible for transporting pollen grains from the stamens of a flower to the stigma of the same flower, or from one flower to another. Without these, the pollen grains would have difficulty reaching their destination and reproduction might not occur. Insects, wind, some mammals and birds, water and man are examples of pollination agents. Pollination can be direct (by self-pollination) or indirect (by crossing with another flower of the same plant or with flowers of different plants of the same species). Direct pollination (Pollen from a flower lands directly on the stigma of that same flower) and Indirect pollination/9 Pollen from a flower lands on the stigma of another flower on the same plant or on a different plant).
publicity
The process of seed dispersal is called dissemination

The process of seed dispersal is called dissemination. This process is extremely important for the seeds to be taken to other places, often far from the plant that originated them, and thus be able to colonize new environments. Dissemination can be carried out: by animals (including humans), by wind, water and by the plant itself (mechanical dissemination). When it finds a place with adequate temperature, humidity and light conditions, germination takes place, that is, the seed becomes a new plant. In the seed, there are specific structures that will give rise to the various organs of the future plant: the radicle (will give rise to the root of the plant), the caulicle (will become the stem of the plant), the bud or plumule (from which the first leaves of the plant). The cotyledons (contain food reserves, which the embryo needs) and the integument (protects the entire seed).
Microorganisms are organisms so small that they

Microorganisms are organisms so small that they are invisible to the naked eye and can only be observed with the help of a microscope. Micro-organisms exist in the most varied habitats: in the air, soil, water, inside our bodies or on the walls of our homes, for example. To develop they need adequate conditions of humidity, temperature, oxygen and nutrients. We can identify several groups of micro-organisms: Protozoa (Trypanosoma brucei - sleeping sickness); Bacteria (Escherichia coli); Viruses(Ebola Virus) and Microscopic Fungi(Mold Fungus). Important micro-organisms for humans: Pathogenic microorganisms (they cause diseases such as flu, pneumonia, athlete's foot and sleeping sickness) and Useful micro-organisms (they are useful in the daily life of human beings, for example, the yeasts that we use to make bread or the bacteria in yogurt).
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895)

Louis Pasteur (1822-1895), was a French scientist of the 19th century, is considered one of the fathers of microbiology, the science that studies microorganisms. Pasteur created the first vaccine against rabies, reducing the mortality associated with this disease, but he is best known for inventing pasteurization, a process used to destroy pathogenic microorganisms present in certain foods.
publicity
Alexander Fleming (Lochfield, August 6, 1881 – London

Alexander Fleming (Lochfield, August 6, 1881 – London, March 11, 1955) was a British biologist, botanist, physician, microbiologist and pharmacologist. Author of several works on bacteriology, immunology and chemotherapy, he became famous as the discoverer of the antimicrobial protein lysozyme, in 1923, and of penicillin, obtained from the fungus Penicillium notatum, in 1928, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 together with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.
With the development of societies and technology

With the development of societies and technology, new threats to the planet also arise. Thinking he is doing his best, man is destroying his home, the Earth, polluting the soil, air and water. The main causes of air pollution are: the burning of fossil fuels; agriculture and livestock production with the consequent emission of gases such as methane and the burning used in agriculture and forest clearing, which release carbon dioxide. The causes of soil pollution: the excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture and livestock; industries that pollute the soil, such as oil refineries, chemical, tanning and textile factories and open-air garbage disposal. The causes of water pollution: waste discharges from the sewage and sanitation system that are not properly treated; the deposit of garbage in rivers, seas and oceans; oil spillage and contamination of underground water with chemical and toxic products.
Ozone
Ozone is a gas composed of molecules with three atoms of oxygen (O3). This gas is distributed in the troposphere, which concentrates about 10% of all ozone, and in the stratosphere, which accumulates most of this gas, about 90%. Ozone found in the troposphere originates from pollutants released into the lower layer of the atmosphere. Ozone present in the stratosphere plays a fundamental role in maintaining life on planet Earth. Distributed in a thin and unstable layer in the stratosphere, between 25 and 30 kilometers from planet Earth, this gas absorbs more than 95% of the dangerous ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun, protecting the Earth from overexposure to these rays, which could affect the entire environmental dynamics of the planet. This decrease in the concentration of O3 in the atmosphere has caused an increase in the amount of ultraviolet rays that reach the earth's surface, causing various impacts to the environment around the world.
publicity
The digestive system

The digestive system is made up of organs that work together to allow the absorption of as many nutrients as possible from the food ingested. It is formed by the following organs: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus. In addition, it is connected to glands that release their secretion inside the digestive tract, they are: salivary glands, pancreas, liver and gallbladder.
The respiratory system
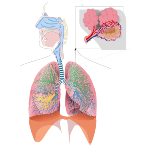
The respiratory system is the set of organs responsible for absorbing oxygen from the air by the body and eliminating carbon dioxide removed from the cells. It is formed by the respiratory tract and the lungs. The organs that make up the airways are: nasal cavities (they have nasal hairs and mucus that retain dust and microorganisms, here the air is warmed, humidified and clean), pharynx (channel for the passage of air to the larynx, it is located the epiglottis that prevents the passage of food to the trachea), larynx (tube lined with cartilage where the sound of our voice is produced), trachea (conducts air to the lungs, is a set of cartilaginous rings lined with small cilia that remove air impurities) and bronchi (conducts air to each of the lungs), bronchioles (branch of the bronchi, small bags - the pulmonary alveoli), lungs (soft, spongy and elastic organs, surrounded by the pleura) and diaphragm (responsible for the respiratory movements).
In the adult body, approximately five liters of blood flow
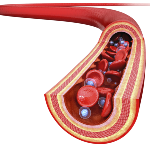
In the adult body, approximately five liters of blood flow, which corresponds to 7% of its weight. It is the cardiovascular or circulatory system, which allows blood to circulate throughout your body, performing the functions: transport (substances, such as oxygen and nutrients); defense of the body against micro-organisms; maintenance of body temperature and water reserve. Your body circulates venous blood (rich in carbon dioxide) and arterial blood (rich in oxygen). Blood is made up of: White Blood Cells (responsible for defending the body against pathogenic microorganisms); Red Blood Cells (carry oxygen from the lungs to the cells, and some carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. They contain hemoglobin which gives blood its red color); Plasma (transports all other constituents of blood, as well as nutrients and some gases, such as carbon dioxide) and Platelets (participate in blood clotting, preventing bleeding).
publicity
Heart is an important muscular organ
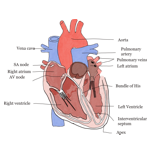
Heart is an important muscular organ, formed mainly by cardiac muscle, which is part of the cardiovascular system. It measures about 12 cm long and 9 cm wide. It weighs, on average, 250 to 300 g in adults. The function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body. The heart is divided into four chambers: two atria (upper cavities where blood comes to the heart) and two ventricles (lower cavities where blood leaves the heart). Between the atria and the ventricles there are valves (right atrioventricular valves and the left atrioventricular valve) that regulate the flow of blood and prevent its reflux, that is, the return of blood from the ventricles to the atria. The cardiac wall is formed by three tunics: pericardium (serous membrane that surrounds the heart), endocardium (thin and smooth membrane that lines the heart cavities internally) and myocardium (responsible for heart contractions).
Blood vessels are of three basic types: veins
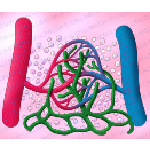
Blood vessels are of three basic types: veins, arteries and capillaries. Veins: carry blood from the body to the heart. Its walls are thinner than arteries. Arteries: carry blood from the heart to the entire body. Its walls are thick and expandable.Capillaries carry blood to tissues to deliver oxygen to cells. They connect arteries and veins.
The circulatory system
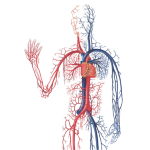
The circulatory system is the set of organs responsible for distributing nutrients to cells and collecting their metabolic excreta to be eliminated by excretory organs. The organs that are part of the circulatory system are: heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph and lymphatic vessels. It is responsible for conducting essential elements to all body tissues: oxygen to cells, hormones (which are released by endocrine glands) to tissues, conducting carbon dioxide for elimination in the lungs, collecting metabolic and cellular excreta, delivery of these wastes to excretory organs such as the kidneys.
publicity
The human urinary system is composed of kidneys
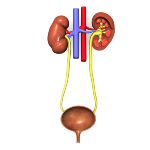
The human urinary system is composed of kidneys, ureters (transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder), urinary bladder (reservoir where urine is stored) and urethra (expels urine to the outside). Blood reaches the kidneys through the renal arteries. The kidneys are the organs located in the posterior portion of the abdominal cavity that filter the toxic substances present in the blood, such as mineral salts, urea and uric acid, being responsible for the formation of urine. They are bean-shaped and consist of a renal capsule, cortex, and medulla. The outer covering of the kidney is called the renal capsule. In the cortex region are located the nephrons, which are responsible for the formation of urine. Finally, we have the renal medulla, which is the innermost part of the kidney, where the presence of the collecting ducts and the nephric loops (structure that makes up the nephron) is verified.
The skin is the largest organ in the human body and
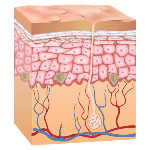
The skin is the largest organ in the human body and is responsible for several functions essential to its functioning. It is this organ that helps us not to lose too much water, in addition to preventing the penetration of various pathogens and protecting against radiation. It is composed of two layers: the epidermis (superficial layer of lesser thickness, and the dermis (internal and thick layer). permanently, where the pores are located); Dermis (layer where the sweat glands, blood vessels and sebaceous glands are located); Sebaceous Glands (produce essential fat to lubricate and waterproof the skin); Sweat Glands (responsible for the production of sweat) and hair.The color of the skin is due to a pigment produced by the epidermis - melanin.
Photosynthesis, a term that means “synthesis using light

Photosynthesis, a term that means “synthesis using light,” is generally defined as the process by which an organism obtains its food. Process of photosynthesis: For the production of organic matter, plants need and carbon dioxide, solar energy, water and mineral salts, and as a result, there is release of oxygen and water vapor to the environment. Sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll, present in the leaves, and provides the energy the plant needs to produce food; The leaves receive carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen and water vapour, and the roots absorb water with dissolved mineral salts from the soil. It is estimated that 40% to 50% of the oxygen present in the atmosphere comes from the algae that live in the oceans and lakes.
publicity
The Skeletal System is made up of fused bones
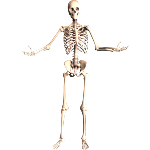
The Skeletal System is made up of fused bones, completed by cartilage and supported by ligaments, tendons and muscles. The human skeleton has 206 bones, which vary in size and shape. They act to support the body, protect vital organs, guarantee movement, produce blood cells and store some mineral salts, such as calcium and phosphorus. Bones are classified according to their shape into five main types: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Joints can be classified as: Synarthroses, Amphiarthroses and Diarthroses and can also be classified according to the material found between the bones: Fibrous joints, Cartilaginous joints and Synovial joints. The skeleton can be divided into: axial (skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum and hyoid bone) and Appendicular (limbs and scapular and pelvic girdles).
Plant transpiration

Plant transpiration is a phenomenon whereby plants lose water in the form of vapour. Although transpiration can occur in any part of the plant exposed to the air, the leaves are the main organ where this process takes place. Transpiration and gaseous exchanges that occur in plants are carried out through the stomata (it is composed of two cells: the stomatal cells or guard cells, which form between them an orifice that opens and closes, the stiole).
Back
